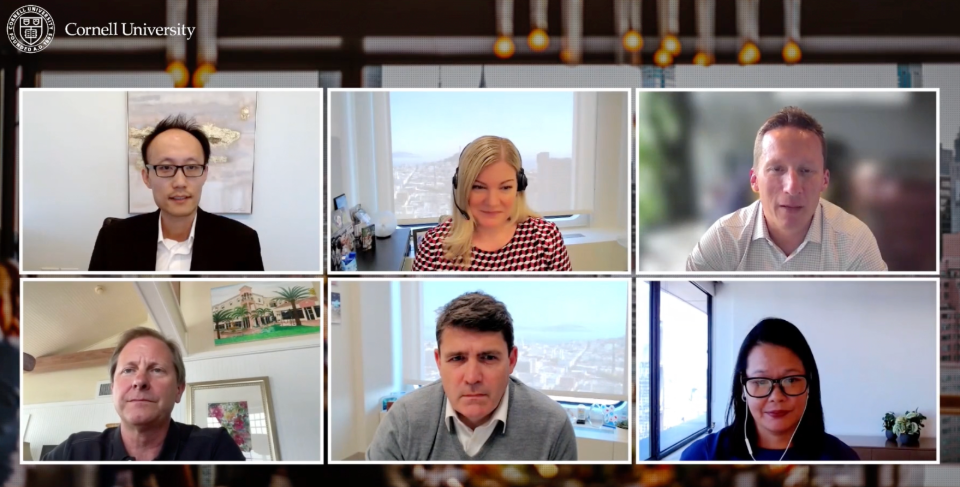
Understanding AI’s impact and ensuring its responsible implementation is essential for board members and senior executives looking to stay ahead in today’s fast-evolving corporate landscape. In a Cornell Keynote, legal professionals from Cleary Gottlieb Steen & Hamilton LLP shared what top management needs to know about navigating the opportunities and challenges AI brings to the boardroom.
- Navigating intellectual property (IP) challenges.
Many generative AI tools feature a public-facing platform in which users enter text prompts to generate new works, such as text, images or songs. However, because these AI models are trained on extensive datasets, often sourced from the internet, AI may create outputs based on copyrighted material.
There are currently around two dozen IP litigation cases in the United States concerning the training and output of generative AI models, including OpenAI’s ChatGPT and Google’s Imagen. “The key question is whether courts will find that the training of these models was fair use or infringing,” explained Angela Dunning, a partner who focuses on commercial litigation.
If the courts rule that AI training methods are not fair use, the development of these tools could change significantly, potentially affecting their availability and competitiveness, especially in the international market.
“The United States Copyright Office has taken the position that AI-generated outputs are not protected under U.S. copyright law because they are not authored by a human,” said Dunning. “This is now in conflict with some jurisdictions around the world, such as the EU’s AI ACT, which may impose restrictions on the use of copyrighted content for AI training and apply them to AI models globally if their output comes into Europe.”
As companies increasingly incorporate AI technology into their workplaces, board members should ensure that their companies have robust policies in place to mitigate IP risks, such as obtaining proper licenses for training data and regularly reviewing compliance with evolving laws. Proactively addressing these challenges can help protect the company’s innovations and preserve its competitive advantage in the market.
- Addressing SEC disclosure requirements.
Erik Gerding, director of the SEC Division of Corporate Finance, recently released a statement signaling AI as a disclosure priority for the SEC and compelling companies to be as detailed as possible in their annual reports, including identifying how the company defines AI and how the technology could benefit the company’s operational outcomes, financial condition and growth potential.
Specificity is crucial for general counsels and legal teams submitting AI disclosures to the SEC. “The SEC is focused on making sure that disclosures public companies make on AI and the opportunities it presents are tailored to that company rather than being a generic boilerplate disclosure,” noted Lillian Tsu, a partner specializing in securities and capital markets transactions.
Tsu also highlights the importance of attending to the material risks of AI technology, as the data that AI generates are predictions, not conclusions. “In other words, the disclosure should not be divorced from what is happening in reality,” added James Hu, a partner who focuses on merger and acquisition (M&A) transactions.
By adhering to these guidelines, companies not only comply with SEC requirements but also foster greater transparency and trust with stakeholders. Comprehensive and tailored AI disclosures reflect a company’s commitment to responsible innovation, offering a clear view of how AI integration aligns with the company’s strategic goals and risk management practices.
- Understanding antitrust implications.
According to D. Bruce Hoffman, a partner whose practice focuses on antitrust enforcement, AI introduces four significant issues on the antitrust front: the use of AI for collusion, unilateral conduct, mergers and compliance with the Robinson-Patman Act.
The use of AI for collusion has garnered the most attention from antitrust enforcers such as the Department of Justice and the Federal Trade Commission due to concerns that AI systems could enable competitors to coordinate pricing or other market behaviors.
“The Department of Justice has drawn an analogy stating that AI, in this context, is no different from a person. If competing companies were to send their cost data to this person who then instructed them to charge the same price, that would constitute collusion. This can potentially lead to antitrust trouble as well as exposure to civil problems,” said Hoffman.
Another issue is the role of AI in unilateral conduct, particularly in monopolization cases. AI systems could make decisions that, while rational, could be seen as anticompetitive if they harm competitors in ways that violate Section 2 of the Sherman Act. The challenge for antitrust enforcers will be determining when an AI’s autonomous actions cross the line from aggressive competition to unlawful conduct.
- Leveraging AI in M&A.
AI is quickly becoming a driver of M&A activities as companies look to strengthen their competitive edge. Benet J. O’Reilly, a partner specializing in mergers and acquisitions, notes that AI is a hot investment area, with firms either developing AI in-house or acquiring third-party tools to integrate into their operations.
This surge in AI-driven M&A is fueled by the need to stay ahead in a rapidly evolving technological landscape. Companies are not only seeking innovative technologies but also the talent and expertise behind them. “Talent acquisitions are crucial because they not only bring valuable technology in-house but also prevent that talent from being available to competitors,” explained O’Reilly.
However, integrating these AI-focused teams into larger, more traditional organizations can be challenging. Companies must strike a balance between maintaining the creativity and agility of these teams while aligning them with broader corporate objectives — a process requires careful planning and a willingness to adapt.
As AI reshapes industries, M&A deals may become more prevalent, with companies increasingly turning to strategic acquisitions to build out their AI capabilities. For executives, understanding the complexities of these transactions will be crucial.
For more insights on approaching AI-related developments in the boardroom, experience the full Keynote “Artificial Intelligence in the Boardroom: What Board and Senior Executives Need To Know” on the eCornell website.
This Keynote is part of a series of discussions leading up to eCornell’s 2025 Board of Directors Forum. Register now for the opportunity to network and share best practices on cybersecurity, supply chains, data and AI, and earn a Cornell Tech Board of Directors Forum certificate from Cornell Tech.
Photo: Clockwise from left: Partners at Cleary Gottlieb Steen & Hamilton LLP James Hu, Angela Dunning, Chase Kaniecki, Lillian Tsu, Benet O’Reilly and D. Bruce Hoffman.


 Steve Sauer at Big D program
Steve Sauer at Big D program Chris Collins at VINCI session
Chris Collins at VINCI session